Recently, Professor Zhao Wei's team has made new progress in the research of antiviral immune regulation. The related research achievements are published online in Science Advance with the title of“RNF39 mediates K48-linked ubiquitination of DDX3X and inhibits RLR-dependent antiviral immunity” (5-year if = 14.094). Shandong University is the independent first and corresponding author unit of this article. Doctoral student Wang Wenwen, postdoctoral Jia Mutian, and assistant researcher Zhao Chunyuan are the co-first authors, and Professor Zhao Wei is the corresponding author.
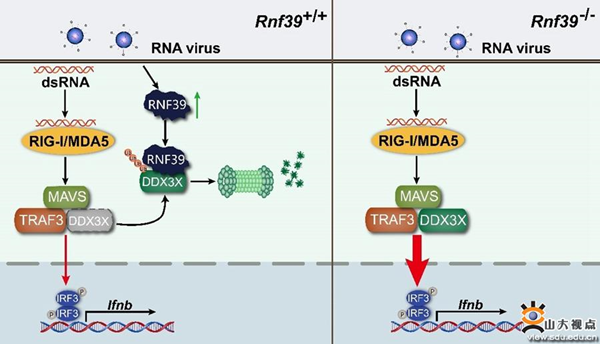
Retinoic acid-induced gene I-like receptors (RLRs) are important RNA recognition receptors. After recognizing viral RNA, they activate the adaptor molecule Mavs, promote the expression of type I interferon, and initiate the antiviral immune response. RLR-dependent signaling pathway plays an important role in antiviral infection and maintaining immune homeostasis; abnormal activation of RLRs is closely related to the occurrence and development of a variety of autoimmune disorders. Therefore, strict regulation of RLRs activation is very important to ensure the rapid elimination of invading virus and avoid self-injury. Ddx3x, a member of the RNA helicase family, is an important adaptor molecule in the RNA virus recognition pathway, which can enhance the innate immune activation against RNA virus by forming Mavs-ddx3x complex; at the same time, ddx3x can recognize HIV-1 ssRNA and promote the elimination of HIV-1.
Therefore, ddx3x is very important for the body to clear the virus. In this study, we found that in the process of virus infection, K48 coupled ubiquitination modification of lysine (K55, K138, and k162) at positions 55, 138, and 162 of ddx3x molecule can occur, and then be degraded by proteasome; rnf39 is the E3 ubiquitin ligase that mediates this process. Rnf39 can inhibit the expression of ddx3x, block the formation of the mavs-ddx3-traf3 complex, inhibit innate immune activation and realize the immune escape of the virus.
Rnf39 gene is located in the MHC-I gene region, and GWAS and SNP analysis have found that rnf39 is closely related to the progress of viral diseases. This study clarified the specific role and molecular mechanism of rnf39 in viral diseases and innate immune regulation; clarified the important role of ddx3x ubiquitination modification in antiviral immune regulation in the process of viral infection; revealed the mechanism of the virus by inducing rnf39 expression, inhibiting immune activity and achieving immune escape; provided a basis for the prevention and treatment of viral diseases and autoimmune diseases New targets.
Professor Zhao Wei's team has been engaged in the research of virus infection and innate immunity for a long time, revealing the activation and regulation mechanism of innate immunity in the process of virus infection; the related research results are published in NAT. Immunol. (2020) Sci.Adv .(2021)、Nat. Commun. (2020,2016, 2014)、J. Exp.Med . (2017)、PNAS.(2016)、 Cell.Rep (2017). The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Newton senior scholar of the British Academy of Medical Sciences.
Article link: https://advances.sciencemag.org/content/7/10/eabe5877






