Recently, professor Yu Shuyan of basic medical college and his team made new progress in The field of depression research, and published a research paper entitled “microrNA-26A-3p Rescues depression-like behaviors in Male rats via Preventing hippocampal neuronalA research paper on anomalies " online in The international academic Journal of The Journal of Clinical Investigation (CAS-1,IF=14.808). Li Ye, PhD candidate, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Shandong University, was the first author, and Yu Shuyan, Professor, Department of Physiology and Pathophysiology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Shandong University, was the corresponding author.
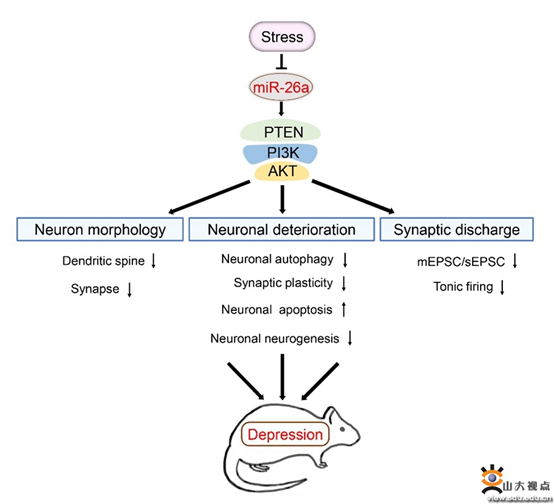
Through high-throughput sequencing analysis of microRNA in dentate Gyrus (DG), We found that Mir-26a-3p was significantly down-regulated in the DG region of hippocampus of chronic stress-induced depression rats. Overexpression of Mir-26a-3p in DG region can effectively improve neuroplasticity disorder and depression-like behavior induced by stress stimulation. Further studies found that, under the action of external stress stimulation, the level of Mir-26a-3p in the hippocampus of rats was significantly decreased, which could lead to the increase of the expression of its downstream target PTEN, and then activate the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, which could lead to synaptic damage of hippocampal neurons by inhibiting autophagy and promoting apoptosis. Whole-cell Recording results further confirmed that the frequency and amplitude of excitatory postsynaptic currents mEPSC and sEPSC of neurons were significantly decreased after mir-26a-3p was knocked out in the DG region, suggesting that synaptic transmission function was weakened and hippocampal neuron network discharge was abnormal, which was ultimately involved in the occurrence of depressive symptoms
Paper link: https://www.jci.org/articles/view/148853